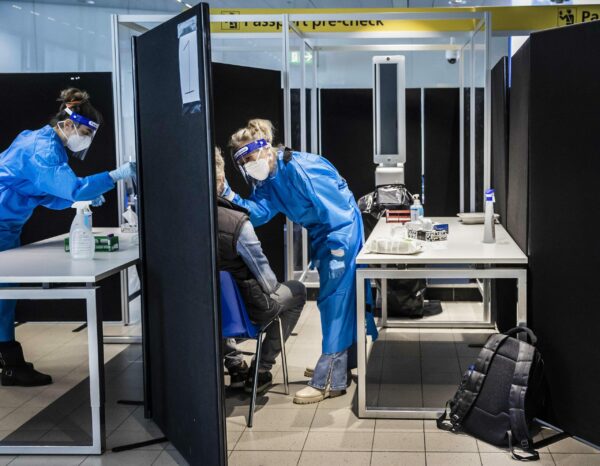
A potential situation is that Omicron makes the Covid less startling, Hadassah’s Prof. Dror Mevorach said.
The omicron variation has 50 changes in general, with 32 transformations on the spike protein alone
Another variation named omicron (B.1.1.529) was accounted for by specialists in South Africa on Nov. 24, 2021, and assigned a “variation of worry” by the World Health Organization two days after the fact. Omicron is exceptionally surprising in that it is by a long shot the most intensely transformed variation at this point of SARS-CoV-2, the infection that causes COVID-19.
Researchers in South Africa currently have proof that the omicron variation of the Covid spreads over two times as fast as the delta variation in that country.
New information distributed on Saturday propose that the Omicron crown variation is more infectious yet not generally so perilous as different variations, as per Prof. Dror Mevorach, a senior doctor from Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center.
The omicron variation has 50 transformations generally speaking, with 32 changes on the spike protein alone. The spike protein – which structures jutting handles outwardly of the SARS-CoV-2 infection – assists the infection with following cells so it can acquire section. It is additionally the protein that every one of the three immunizations at present accessible in the U. S. use to instigate defensive antibodies. For correlation, the delta variation has nine transformations. The bigger number of changes in the omicron variation might imply that it very well may be more contagious and additionally better at dodging invulnerable security – a possibility that is very disturbing.
“This wave appears to be a lot quicker than the delta wave. What’s more we thought the delta wave was super quick. It’s mind blowing,” says Juliet Pulliam, who coordinates South Africa’s DSI-NRF Center of Excellence in Epidemiological Modeling and Analysis at Stellenbosch University.
“We need to say this with a ton of alert, yet assuming we check out the as of now accessible data, there is motivation to accept that the variation is spreading quick, however perhaps it isn’t the case perilous,” Mevorach said.
While the uncommonly big number of changes in the omicron variation is amazing, the rise of one more SARS-CoV-2 variation isn’t sudden.
Through regular choice, arbitrary changes gather in any infection. This interaction is accelerated in RNA infections, including SARS-CoV-2. In the event that and when a bunch of transformations gives an endurance benefit to a variation over its archetypes, the variation will out-contend any remaining existing infection variations.
The investigation, introduced at a logical meeting Friday, proposes the omicron variation is profoundly contagious and furthermore more fit for avoiding the resistant framework than delta.
“It appears as though it very well might be more contagious than delta,” says Pulliam, who drove the investigation. “There’s an enormous measure of vulnerability in the investigation, yet I would say it looks likely.”
A few specialists proposed that assuming Omicron is more irresistible yet milder, it could make crown more like influenza. Mevorach concurred, saying “it would truly be uplifting news for the world. I believe that we have had signs of inoculated individuals getting tainted, however apparently their infection is gentle.”
One potential clarification for how popular variations with various changes arise is through drawn out contamination in a patient whose invulnerable framework is smothered – a circumstance that can prompt fast popular advancement. Scientists have speculated that a portion of the previous SARS-CoV-2 variations, like the alpha variation, may have originated from a perseveringly tainted patient. Nonetheless, the surprising heavenly body and various transformations in the omicron variation make it altogether different from any remaining SARS-CoV-2 strains, which brings up issues regarding how it came to fruition.
On Thursday, Pulliam and her associates additionally distributed a review web based appearance that reinfections are more probable with omicron than with the delta or the beta variations. The review couldn’t assess the extent of this change — that is, the amount more probable reinfections will be — yet it shows firmly that this new variation is more fit for bypassing antibodies produced by an earlier contamination than past variations.
“We may have to acknowledge that certain individuals will become ill, and treat them with the antiviral medicines that are going to open up, or the immunizations may be somewhat changed to be more compelling,” he said. “In any case, I’m not completely certain that we should do it. The primary choice may be sufficient.”
How the delta variation became prevailing around the world
Delta is somewhere in the range of 40% and 60% more contagious than the alpha variation and almost twice as contagious as the first SARS-CoV-2 infection originally recognized in China.
The delta variation’s elevated contagiousness is the essential motivation behind why specialists accept it had the option to out-contend different variations to turn into the predominant strain.
A critical variable in viral wellness is its replication rate – or how rapidly an infection can make more duplicates of itself. The delta variation imitates quicker than past SARS-CoV-2 variations, and a not-yet-peer-assessed concentrate on assessed that it produces multiple times more infection particles than its archetypes.
Distinguished seven days prior and prone to outcompete delta
Last week, researchers in South Africa and Botswana distinguished the new omicron strain of the Covid, one with around 50 changes across its genome. Conversely, different variations, like delta, have less than 20 transformations.
Since Nov. 24, when the variation was accounted for to the World Health Organization, wellbeing authorities have recognized omicron in excess of twelve nations across something like five mainlands. The variation represents a “extremely high” hazard, the WHO said on Monday.
In the course of recent weeks, omicron has spread to somewhere around seven of South Africa’s nine territories, rapidly surpassing the nation’s flare-up and accordingly, it shows up, outcompeting delta, says virologist Pei-Yong Shi of the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston.

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks ago
 Health3 weeks ago
Health3 weeks ago
 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago
 Sports3 weeks ago
Sports3 weeks ago
 Science3 weeks ago
Science3 weeks ago
 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks ago
 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks ago
 Science1 week ago
Science1 week ago