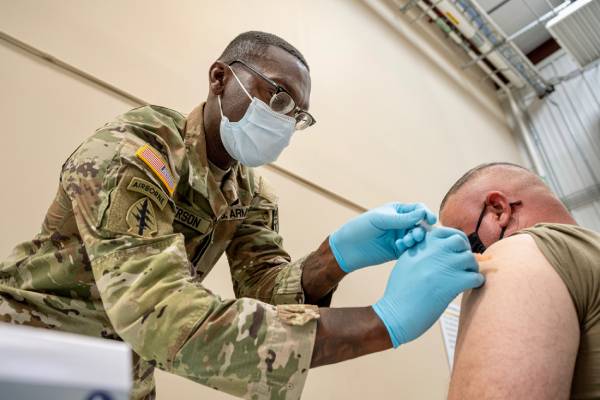
US Army liable to report immunization powerful against all variations, including omicron.
It has finished stage 1 of human preliminaries, with second and third stages remaining.
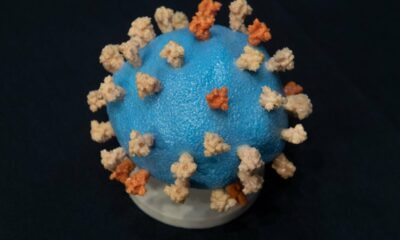
This is a spike ferritin nanoparticle antibody.
In half a month, researchers at the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research are relied upon to declare an immunization that is successful against all SARS and COVID-19 variations, including Omicron.
Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (WRAIR) researchers are relied upon to declare an antibody viable against all COVID variations, including omicron which has the world stressed as of now. The immunization, which has been being developed for right around two years, is probably going to be uncovered in half a month’s time.
The immunization has been underway for right around two years, Defense One revealed, later the military accepted its first DNA sequencing of the COVID-19 infection in mid 2020. The military at a beginning phase endeavored to make an immunization that would be powerful against various variations, the media source announced.
Specialists got an example in mid 2020 and zeroed in endeavors on fostering an antibody that would neutralize possible variations. After two years, the underlying outcomes show guarantee.
Dr. Kayvon Modjarrad, overseer of Walter Reed’s irresistible infections branch told Defense One said the antibody has had “positive outcomes” at the preliminary stage.
From a beginning phase, since the military accepted its first COVID infection DNA sequencing in 2020, they endeavored to make an immunization that could be powerful against all emanant variations. At present, reports propose that the immunization has shown positive outcomes in the underlying testing stages.
The stage 1 human preliminaries initiated April 2021. Researchers hailed the early information as empowering and will distribute last stage 1 review results once they complete the investigation.
“Walter Reed’s Spike Ferritin Nanoparticle COVID-19 antibody, or SpFN, finished creature preliminaries recently with positive outcomes,” he said.
Recently, creature preliminaries were likewise reassuring. Dr. Kayvon Modjarrad, the overseer of the irresistible infections branch at Walter Reed expressed that stage 1 of testing against omicron and different variations was finished in December, and appeared to be encouraging. This news shows up promptly, since research proposes that the omicron variation has dodged the insurance presented by existing antibodies.
The hypothesis behind the advancement of the Spike Ferritin Nanoparticle Platform (SpFN) immunization sets that presenting numerous duplicates of spike proteins in an “requested style” may demonstrate key to making a “intense and wide reaction.”
In front of stage 2 and 3 preliminaries, Modjarrad remarked, “We really want to assess it in reality setting and attempt to see how does the immunization act in a lot bigger quantities of people who have as of now been inoculated with something different initially…or currently been wiped out.” There will be a few perceptions of how the new antibody associates with individuals who have been recently immunized with the items created by Moderna, Pfizer/BionTech, and Johnson and Johnson.
“This immunization hangs out in the COVID-19 antibody scene,” said Dr. Kayvon Modjarrad, overseer of the Emerging Infectious Diseases Brance at WRAIR. “The redundant and requested showcase of the Covid spike protein on a multi-confronted nanoparticle may animate insusceptibility so as to convert into fundamentally more extensive security.”
Contrasted with these different immunizations, the one being created by the US armed force is a spike ferritin nanoparticle antibody. It has a protein formed like a soccer ball, and having 24 appearances. Subsequently, it can get connected to the spikes of various COVID variations on numerous different appearances of the protein.
Pre-clinical investigations distributed in Science Translational Medicine demonstrate insurance against the first strain of COVID-19 just as variations that rose up out of the first SARS-CoV-1 infection from 2002.
Presently, the inquiry is on for an accomplice to assist roll with trip the antibody. This across the board antibody is being made watching out for what’s to come. Since the infection is relied upon to change, there are probably going to be other developing variations too. The methodology that this military made antibody takes, could assist individuals with getting ready against this possibility.
One of the main focal points concerns how the immunization connects with individuals who have effectively gotten an inoculation or had a past contamination.

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks ago
 Health3 weeks ago
Health3 weeks ago
 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago
 Sports3 weeks ago
Sports3 weeks ago
 Science3 weeks ago
Science3 weeks ago
 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks ago
 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks ago
 Science1 week ago
Science1 week ago