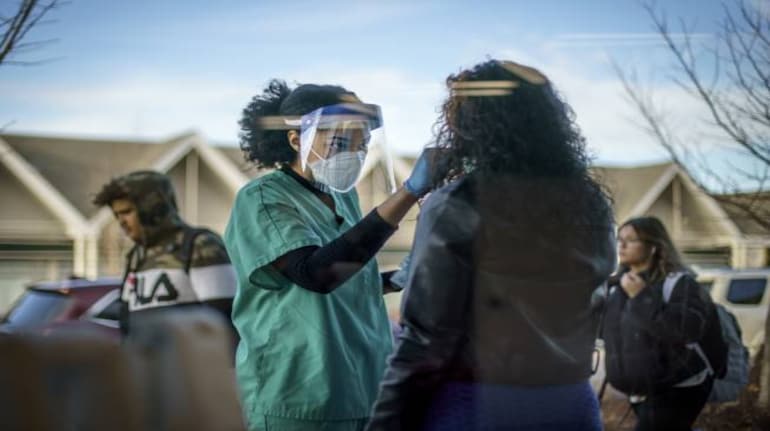
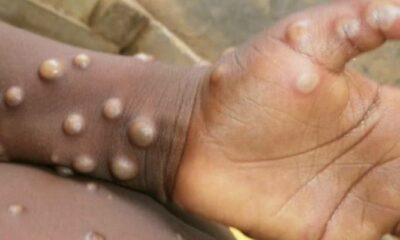
Researchers are seeing signs that COVID-19′s disturbing omicron wave might have topped in Britain and is going to do likewise in the U.S., so, all things considered cases might begin dropping off significantly.
Omicron could be set out toward a quick drop in light of the fact that the variation has demonstrated so ridiculously infectious that it might as of now be running out of individuals to contaminate.
“It will descend as quick as it went up,” said Ali Mokdad, an educator of wellbeing measurements sciences at the University of Washington in Seattle.
The explanation: The variation has demonstrated so stunningly infectious that it might as of now be running out of individuals to contaminate, only a month and a half after it was first identified in South Africa.
“There are still a many individuals who will get tainted as we plunge the slant on the rear,” said Lauren Ancel Meyers, head of the University of Texas COVID-19 Modeling Consortium, which predicts that revealed cases will top inside the week.
Simultaneously, specialists caution that much is as yet dubious with regards to how the following period of the pandemic may unfurl. The leveling or ebbing in the two nations isn’t occurring wherever simultaneously or at a similar speed. What’s more weeks or long periods of hopelessness actually lie ahead for patients and overpowered medical clinics regardless of whether the drop-off happens.
In Britain, in the mean time, new COVID-19 cases dropped to around 140,000 per day somewhat recently, subsequent to soaring to in excess of 200,000 per day sooner this month, as indicated by government information.
Indeed, he said, by the college’s mind boggling estimations, the genuine number of new day by day contaminations in the U.S. — a gauge that incorporates individuals who were rarely tried — has effectively topped, hitting 6 million on Jan. 6.
Kevin McConway, a resigned teacher of applied measurements at Britain’s Open University, said that while cases are as yet ascending in spots, for example, southwest England and the West Midlands, the episode might have topped in London.
Contrasts among Britain and South Africa, including Britain’s more seasoned populace and the inclination of its kin to invest more energy inside in the colder time of year, could mean a bumpier episode for the nation and different countries like it.
The figures have raised expectations that the two nations are going to observe what occurred in South Africa, where the wave peaked at record highs and afterward fell essentially about a month after the fact.
“We are seeing an unmistakable tumbling off of cases in the U.K., yet I might want to see them fall a lot further before we know whether what occurred in South Africa will occur here,” said Dr. Paul Hunter, an educator of medication at Britain’s University of East Anglia.
On Tuesday, the World Health Organization said there have been 7 million new COVID-19 cases across Europe in the previous week, considering it a “tsunami clearing across the area.” WHO refered to displaying from Mokdad’s gathering that predicts half of Europe’s populace will be contaminated with omicron inside around two months.
Shabir Mahdi, senior member of wellbeing sciences at South Africa’s University of Witwatersrand, said European nations that force lockdowns will not really gotten through the omicron wave with less diseases; the cases may simply be fanned out throughout a more extended timeframe.
Then again, British specialists’ choice to take on negligible limitations against omicron could empower the infection to tear through the populace and run its course a lot quicker than it may in Western European nations that have forced harder COVID-19 controls, like France, Spain and Italy.
“There will presumably be some high points and low points en route, however I would trust that by Easter, we will be out of this,” Hunter said.
“The following not many weeks will be ruthless on the grounds that in outright numbers, such countless individuals are being tainted that it will pour out over into ICUs,” Jha said.
“Toward the finish of this wave, undeniably more individuals will have been tainted by some variation of COVID,” Meyers said. “Eventually, we’ll have the option to define a boundary – and omicron might be that point – where we progress based on what is a devastating worldwide danger to something a considerably more reasonable illness.”
Mokdad in like manner cautioned: “It will be an intense half a month. We need to settle on hard choices to allow specific fundamental laborers to keep working, realizing they could be irresistible.”
That is one conceivable future, she said, however there is likewise the chance of another variation – one that is far more regrettable than omicron – emerging.

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks ago
 Health3 weeks ago
Health3 weeks ago
 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago
 Sports3 weeks ago
Sports3 weeks ago
 Science3 weeks ago
Science3 weeks ago
 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks ago
 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks ago
 Science1 week ago
Science1 week ago