Health
According To Dietitian , Here Are Finest Food To consume Daily For Lengthy Life
Published
3 years agoon
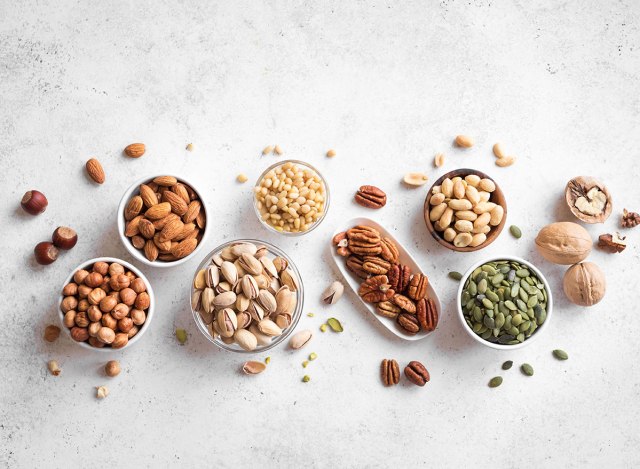

An every day serving of these crunchy pieces can be beneficial.
Carrying on with a long and sound life is an objective that the majority of us endeavor to accomplish. And keeping in mind that factors that are all the way out of our control-like our hereditary qualities can have a major influence in whether we will live to encounter our 100th birthday celebration, different elements like our dietary decisions can likewise assume a part.
There’s an explanation the Mediterranean diet has been named the life span diet. Research shows that individuals who follow the eating plan – which leans toward new food varieties over handled – will generally carry on with long lives, yet lengthy, sound lives. Not incidentally, it’s additionally the one generally followed by individuals who live in the Blue Zones, those five locales of the world with the most noteworthy grouping of solid centenarians.
Following the Mediterranean dietary examples which centers around olive oil, nuts, seeds, vegetables, fish, and produce-will in general bring about an increment in their future, partially on account of the calming benefits that this dietary example offers. Thusly, standards of this diet are intermittently hauled as a “wellspring of youth,” of sorts.
The examinations
After specialists led a meta-investigation assessing 20 examinations, results propose that a 28 grams each day expansion in nut admission was related with a general 22 percent decline in the gamble of early demise because of any reason. Results likewise showed a diminished gamble of early demise because of respiratory illnesses, diabetes, neurodegenerative sickness, irresistible infection, and kidney sickness.
With regards to pecans explicitly, an enormous observational review utilizing information that was gathered more than 20 years showed that eating somewhere around five servings of pecans consistently is connected to a decreased gamble of early passing in any event, for individuals who followed “sub-par” diet characteristics. As per the outcomes, for each 0.5 serving expansion in pecan utilization each day, members had a 9% lower hazard of early demise.
Different information showed that eating a day by day modest bunch of nuts brought about a 20 percent hazard decrease of early passing north of a 30-year time span contrasted with the people who didn’t consume nuts
Nuts
It’s not difficult to see the reason why nuts land on each rundown of superfoods. “They’re a thick wellspring of supplements that can uphold our insusceptible framework and digestion, balance irritation and stomach wellbeing, advance mind and heart wellbeing, as well as deal disease preventive properties,” says Stacy Kennedy, an enrolled dietitian in Wellesley, Massachusetts. No big surprise they advance life span.
In a review distributed in BMC Medicine, specialists enrolled in excess of 7,000 grown-ups between the ages of 55 and 80 who were at high gamble for cardiovascular infection and requested that they follow one of three weight control plans: a Mediterranean eating regimen enhanced with additional nuts, a similar eating routine yet with extra additional virgin olive oil rather than nuts, or a low-fat eating regimen. Following five years, the individuals who consumed multiple one-ounce servings of nuts each week had a 39 percent lower generally mortality hazard than the non-nut eaters. Indeed, throughout the review, the nut eaters had the most reduced complete passing gamble. “Nuts give us fiber, protein, sound fats and key nutrients and minerals like omega-3s, vitamin E, calcium and selenium,” Kennedy says.
Organic products
There’s no such thing as an awful natural product . They generally offer an assortment of invulnerable strong, mitigating and hostile to maturing properties like L-ascorbic acid, potassium and phytochemicals, those really great for-you intensifies found in plants, Kennedy says. However, “berries are especially useful, as they are low in sugars, high in fiber and wealthy in supplements,” she adds. “The energetic shading is one way you can perceive they are really great for you. The blue-purple group of supplements, as in many berries, have one of a kind properties for resistance, mind wellbeing and cardiovascular wellbeing.” In a review distributed in Applied Psychology, Nutrition and Metabolism, solid individuals between the periods of 66 and 70 who drank concentrated blueberry squeeze consistently showed upgrades in cerebrum action. The review proposes their memory likewise gotten to the next level.
Green tea
On the off chance that you knew worse, you could figure the key to returning to the past on maturing can be found in a pot of green tea. You wouldn’t be distant. Research has connected green tea to a lower hazard of coronary illness, malignant growth, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s and stoutness. Nothing unexpected, then, at that point, that one investigation of more seasoned Japanese grown-ups found that the individuals who drank the most green tea – at least five cups every day – were 26% less inclined to bite the dust during the seven-year concentrate on period than the people who drank one cup a day. What is it regarding green tea? Supplement rich food varieties that are high in cell reinforcements – like green tea – have been connected with longer telomeres. Like the plastic tips of a shoestring, telomeres can be found toward the finish of chromosomes and safeguard DNA. They normally abbreviate as we age, yet the cycle can be sped up by things like smoking, stress and terrible eating routine.
Entire grains
Eating all the more entire grains – think earthy colored rice, wheat, cereal, popcorn, couscous, quinoa – may decrease the gamble of early demise, as per an enormous audit of studies distributed in Circulation. The analysts observed that individuals who ate around four servings of entire grains each day had a lower hazard of biting the dust during the 40-year concentrate on period, contrasted and the people who ate pretty much nothing or none by any means. The medical advantages are accepted to be an aftereffect of the great fiber found in entire grain food sources, which might bring down cholesterol creation. Furthermore, says Kirkpatrick, “entire grains can supplant white, refined grains, which contrarily affect insulin, glucose and satiation.”
Dull mixed greens
Not that you really want one more motivation to fill your plate with verdant green vegetables, yet here it is: Eating spinach, kale, chard, collards, lettuce and such consistently may slow progress in years related mental deterioration, as per a review in the diary Neurology. Scientists analyzed review members who ate around 1½ servings of greens a day with the individuals who ate under a serving a day and observed that the pace of mental degradation among the people who consumed the most was what might be compared to being 11 years more youthful (as far as cerebrum wellbeing).
Vegetables
Individuals who live in the Blue Zones – regardless of whether it’s Okinawa, Japan; Sardinia, Italy; Nicoya, Costa Rica; Ikaria, Greece; or Loma Linda, California – feel weak at the knees over plant-based food sources, particularly the numerous peas, beans and lentils that are essential for the vegetable family. These centenarians eat somewhere around four fold the number of beans as Americans do by and large.
“Vegetables are low in fat and high in protein, folate, iron, potassium and magnesium,” Kirkpatrick says. That is not all. A survey distributed in the diary Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition observed that beans are firmly connected to a decreased gamble of ongoing sicknesses like cardiovascular infection, disease and diabetes.
Step by step instructions to add more nuts to your eating routine
Nuts are an optimal food to zero in on the off chance that you are attempting to add a long time to your life, as they are a simple food to remember for your eating routine. While some “superfoods” can be trying to slip into a bustling way of life, nuts are entirely convenient and are a straightforward backup to plates of mixed greens, cereal, yogurt parfaits, and a lot more dishes.
While eating a small bunch of nuts consistently won’t be the mysterious wellspring of youth, incorporating these crunchy pieces in your eating regimen alongside partaking in actual work, keeping a sound weight, and overseeing pressure might assist you with living to see your centennial birthday.
Health
Fruits High in Protein: A Surprising Nutritional Boost
Published
4 months agoon
January 20, 2025
When thinking of protein sources, fruits might not top the list. However, certain fruits can contribute a surprising amount of this essential macronutrient. While they can’t replace traditional high-protein foods like beans, legumes, or meats, these fruits provide a valuable combination of protein, fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. Here’s a closer look at protein-rich fruits and their nutritional benefits.
Why is Protein Important?
Protein plays a crucial role in maintaining satiety, tissue repair, and muscle growth. High-protein diets are widely known for aiding weight loss and supporting a healthy lifestyle. Recently, plant-based diets have gained attention for their weight loss benefits and overall health advantages.
Registered dietitian Natalie Rizzo emphasizes that fruit protein should be seen as an addition rather than a primary source. “Every gram of protein counts, especially in a plant-forward diet,” she says. Most people need at least 20 grams of protein per meal, and fruits can be a small yet beneficial contributor.
Protein-Rich Fruits
Here are some fruits that stand out for their protein content, with each providing 1 gram or more per serving.
Passion Fruit
- Protein: 5 grams per cup of raw fruit
- Known for its aromatic, jelly-like golden pulp, passion fruit is also rich in fiber, calcium, and vitamins A and C. It can be eaten raw, added to yogurt, or blended into drinks.
Jackfruit
- Protein: 2.8 grams per cup of raw slices
- A relative of figs and breadfruit, jackfruit can be eaten ripe as a sweet fruit or unripe as a meat alternative in plant-based dishes.
Pomegranate
- Protein: 2.9 grams per cup of arils (seeds)
- Pomegranate seeds are packed with antioxidants, dietary fiber, and anti-inflammatory fatty acids beneficial for heart health.
Apricots
- Protein: 2.3 grams per cup of fresh slices; 4.4 grams per cup of dried halves
- This fiber-rich stone fruit also provides antioxidants, iron, and vitamins C, E, B6, and A. Fresh or dried, apricots are a delicious and nutritious snack.
Blackberries
- Protein: 2 grams per cup of raw fruit
- Blackberries are rich in antioxidants that may reduce cancer risk and improve gut health due to their high fiber content.
Guava
- Protein: 1.4 grams per fruit
- This tropical fruit offers antioxidants, vitamin C, potassium, and fiber. Its sweet-tart flavor makes it versatile for eating raw, blending into smoothies, or making jams.
Raisins
- Protein: 1.4 grams per 1.5-ounce box
- Raisins are small but mighty, offering fiber, potassium, and heart health benefits. They make a convenient and nutrient-dense snack, but portion control is key due to their calorie content.
Citrus Fruits
- Protein: 1.2 grams per orange; 2.3 grams per grapefruit
- Famous for their vitamin C content, oranges and grapefruits also deliver fiber, potassium, and hydration while being low in calories.
Cantaloupe
- Protein: 1.3 grams per cup of cubed fruit
- A standout for its high vitamin A content, cantaloupe provides 40% of the daily recommended intake per cup. It’s an excellent addition to fruit salads, smoothies, or desserts.
Incorporating Fruits Into a Protein-Rich Diet
While fruits shouldn’t be relied on as a primary protein source, they can complement a balanced diet rich in beans, nuts, seeds, and other plant-based proteins. Their added benefits—like vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber—make them a healthy, versatile choice.
Whether you’re blending blackberries into a smoothie, topping yogurt with passion fruit pulp, or snacking on a handful of raisins, these protein-rich fruits are a simple way to enhance your diet while satisfying your sweet tooth.
Health
Coffee and Tea Drinking May Reduce the Risk of Some Cancers: Research
Published
5 months agoon
December 25, 2024
Drinking a cup of Joe or some tea for the holidays may be a good thing!
A study reviewed in the journal of the American Cancer Society found that people who drink either tea or coffee have a slightly lower risk of head and neck cancers, though it remains unclear if the drinks themselves directly reduce the risk.
Researchers analyzed data from 14 individual studies involving over 9,500 people with head and neck cancers and over 15,000 people without, compiled by the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology Consortium.
The findings showed that individuals who drank less than four cups of caffeinated coffee daily and less than a cup of tea had a 17% and 9% lower chance, respectively, of developing head or neck cancer overall.
The study also highlighted that coffee drinkers had a reduced risk of developing oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers located in the middle part of the throat, according to Yale Medicine. Meanwhile, tea drinkers who consumed less than a cup daily showed a lower risk of hypopharyngeal cancer, which affects the bottom part of the throat, per Johns Hopkins Medicine.
“While there has been prior research on coffee and tea consumption and reduced risk of cancer, this study highlighted their varying effects with different sub-sites of head and neck cancer, including the observation that even decaffeinated coffee had some positive impact,” said Dr. Yuan-Chin Amy Lee, senior author of the study from Huntsman Cancer Institute and the University of Utah School of Medicine, as reported by The Guardian.
“Perhaps bioactive compounds other than caffeine contribute to the potential anti-cancer effect of coffee and tea,” Lee added.
However, drinking more than one cup of tea daily was linked to a higher risk of laryngeal cancer, which forms in the larynx, the part of the throat responsible for controlling the vocal cords, according to the National Cancer Institute (NCI).
The study also acknowledged limitations, as participants self-reported their findings and were not asked about the specific types of tea or coffee consumed. Additional unaccounted factors may have influenced the results as well.
“In observational studies, it is very difficult to totally eliminate confounding effects, for example, of tobacco and alcohol from the statistical analysis,” Tom Sanders, a professor emeritus of nutrition and dietetics at King’s College London, told The Guardian.
“Consequently, people who drink a lot of coffee and tea may be more likely to avoid other harmful behaviors such as drinking alcohol and using tobacco and so may be at a lower risk of these cancers for other reasons,” added Sanders, who was not involved in the study.
Health
How the brain makes complex judgments based on context
Published
5 months agoon
December 16, 2024
We frequently face difficult choices in life that are impacted by a number of variables. The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) and the dorsal hippocampus (DH) are two key brain regions that are essential for our capacity to adjust and make sense of these unclear situations.
According to research conducted by researchers at the University of California Santa Barbara (UCSB), these regions work together to resolve ambiguity and facilitate quick learning.
Decision-making that depends on context
The results, which were released in the journal Current Biology, offer fresh perspectives on how certain brain regions assist us in navigating situations that depend on context and modifying our behavior accordingly.
According to UCSB neuroscientist Ron Keiflin, senior author, “I would argue that that’s the foundation of cognition.” That’s what prevents us from acting like mindless machines that react to stimuli in the same way every time.
“Our ability to understand that the meaning of certain stimuli is context-dependent is what gives us flexibility; it is what allows us to act in a situation-appropriate manner.”
Decision-making context
Think about choosing whether or not to answer a ringing phone. What you say depends on a number of variables, including the time of day, who might be calling, and where you are.
The “context,” which influences your choice, is made up of several components. The interaction between the OFC and DH is what gives rise to this cognitive flexibility, according to Keiflin.
Planning, reward valuation, and decision-making are linked to the OFC, which is situated directly above the eyes, whereas memory and spatial navigation depend on the DH, which is positioned deeper in the brain.
According to Keiflin, both areas contribute to a mental representation of the causal structure of the environment, or a “cognitive map.” The brain can model outcomes, forecast outcomes, and direct behavior thanks to this map.
Despite their significance, up until now there had been no systematic testing of the precise functions of these regions in contextual disambiguation, which determines how stimuli alter meaning based on context.
Contextualizing auditory stimuli
In order to find out, the researchers created an experiment in which rats were exposed to aural cues in two distinct settings: a room with bright lighting and a chamber with no light. There was a context-dependent meaning for every sound.
For instance, one sound indicated a reward (sugar water) only when it was light, and another only when it was dark.
The rats eventually learnt to link each sound to the appropriate context, and in one situation they showed that they understood by licking the reward cup in anticipation of a treat, but not in the other.
The OFC or DH was then momentarily disabled during the task by the researchers using chemogenetics. The rats’ ability to use context to predict rewards and control their behavior was lost when the OFC was turned off.
Disabling the DH, however, had minimal effect on performance, which was unexpected considering its well-established function in memory and spatial processing.
Enhanced learning from prior knowledge
For learning new context-dependent interactions, the DH proved essential, but it appeared to be unnecessary for recalling previously learned ones.
“If I walked into an advanced math lecture, I would understand – and learn – very little. But someone more mathematically knowledgeable would be able to understand the material, which would greatly facilitate learning,” Keiflin explained.
Additionally, the rats were able to pick up new relationships far more quickly after they had created a “cognitive map” of context-dependent interactions. The duration of training decreased from more than four months to a few days.
Brain areas cooperating
By employing the same chemogenetic strategy, the researchers discovered that the rats’ capacity to use past information to discover new associations was hampered when the OFC or DH were disabled.
While the DH allowed for the quick learning of novel context-dependent relationships, the OFC was crucial for using contextual knowledge to control immediate action.
This dual role emphasizes how these brain regions assist learning and decision-making in complementary ways.
Education and neuroscience Implications
According to Keiflin, neuroscience research frequently overlooks the well-established psychological and educational theories that prior information affects learning.
Knowing how the brain leverages past information to support learning could help develop educational plans and therapies for people who struggle with learning.
The study clarifies the different functions of the DH and OFC as well. In order to acquire new relationships, the DH is more important than the OFC, which aids in behavior regulation based on contextual knowledge.
These areas work together to help the brain adjust to complicated, dynamic surroundings.
Brain’s Capacity to make Decisions based on context
The study emphasizes how crucial contextual knowledge is for managing day-to-day existence. Human cognition is based on the brain’s capacity to resolve ambiguity, whether it be while choosing whether to answer a ringing phone or when adjusting to new knowledge.
This work highlights the complex processes that facilitate learning and decision-making while also advancing our knowledge of brain function by elucidating the functions of the OFC and DH.
This information creates opportunities to investigate the potential roles that disturbances in these systems may play in disorders like anxiety or problems with decision-making.
Since this type of learning is most likely far more reflective of the human learning experience, Keiflin stated that “a better neurobiological understanding of this rapid learning and inference of context-dependent relations is critical, as this form of learning is probably much more representative of the human learning experience.”
The results open the door for future studies on the interactions between these brain areas in challenging, real-world situations, which could have implications for mental health and education.