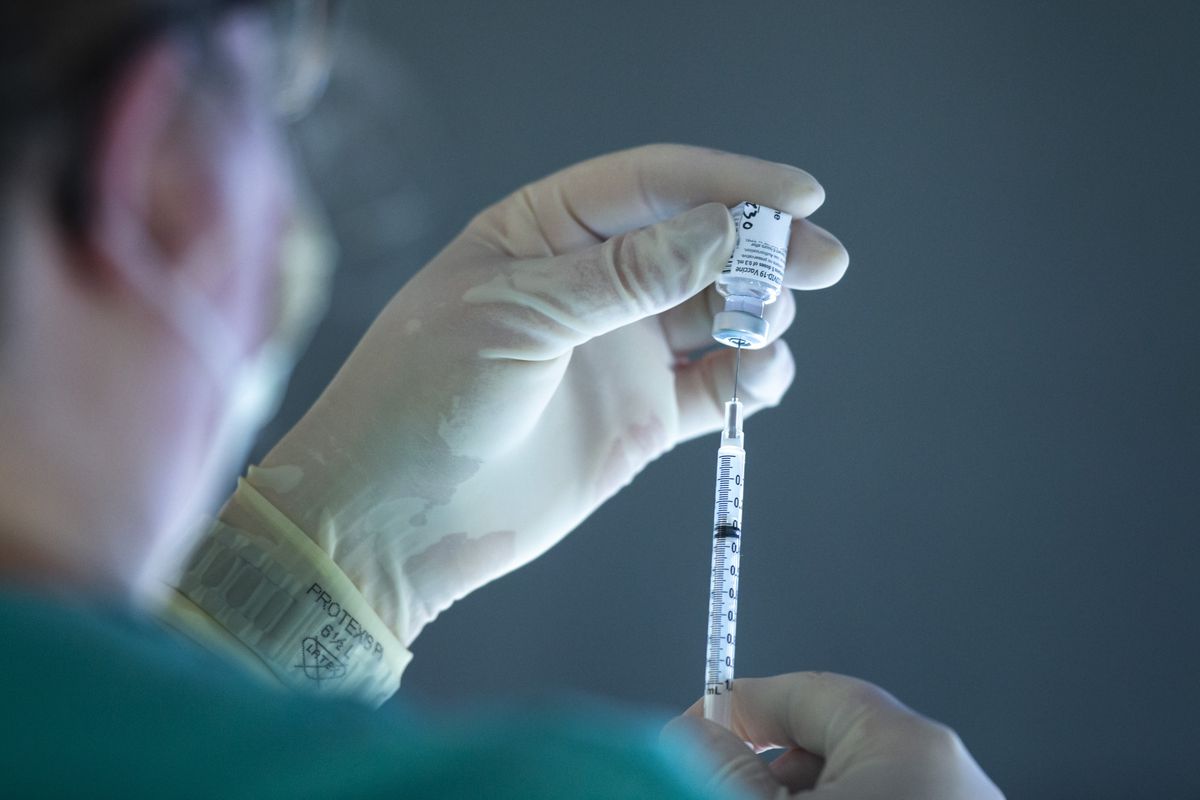
Clinical specialists caution the moving toward influenza season could be especially extreme, reestablishing fears of a potential “twindemic,” with COVID-19 actually spreading in the Chicago region and the nation over.
In readiness, wellbeing authorities are encouraging the general population to get immunized against influenza quickly. The following are eight things to think about the forthcoming influenza season and having your yearly influenza chance during the pandemic:
1.After a significantly gentle influenza season last year, this one may be unpleasant.
Flu was at record low levels last year across the United States, generally because of concealing and social distance conventions in the midst of the pandemic.
Yet, that implies many individuals weren’t presented to influenza last season and didn’t have the chance to help their resistance. Simultaneously, some pandemic limitations have been slackened or dropped, however COVID-19 is as yet flowing, said Dr. Jacqueline Korpics, the Cook County Department of Public Health’s clinical chief for COVID-19.
“There is concern this will be a particularly terrible influenza season because of extricating of alleviations, the way that large numbers of us were not uncovered last year because of COVID alleviations and in light of the fact that flu will be flowing all the while with COVID,” she said. “So people might actually get both simultaneously, which could prompt more extreme sickness and more passings.”
The new flood in nearby instances of another respiratory sickness — respiratory syncytial infection or RSV — may likewise be a harbinger of an approaching terrible influenza season, said Dr. Kelly Michelson, educator of pediatrics and overseer of the Center for Bioethics and Medical Humanities at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine.
“On the off chance that influenza acts like RSV, we ought to plan for heaps of disease,” she said.
2.This present time is a decent opportunity to have influenza chance.
In a perfect world, everybody would be inoculated against seasonal influenza before the finish of October, as per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Korpics said September — this moment — is an extraordinary opportunity to get inoculated against flu.
“Try not to stand by,” she said.
Michelson concurred.
“Influenza immunizations are right now accessible,” she said. “Go get your yearly influenza immunization now.”
3.The COVID-19 shot and influenza antibody can be controlled simultaneously.
“You can get a COVID-19 antibody and different immunizations at a similar visit,” the CDC says on its site. “You at this point don’t have to stand by 14 days between immunizations.”
The organization adds that incidental effects after COVID-19 inoculation are for the most part a similar when given alone or with different vaccinations.
“You can get (antibodies) around the same time,” Korpics said. “We need you to be secured and to ensure people around you who are particularly defenseless against flu and COVID. Try not to let yourself or everyone around you experience the ill effects of a preventable ailment. The two antibodies are protected and, as a general rule, there are not many individuals with contraindications to one or the other immunization.”
4.Get these antibodies to ensure yourself — and to assist the individuals who with getting inoculated.
In spite of the fact that kids under 12 can’t get the COVID-19 antibody yet, most can get vaccinated against influenza, and wellbeing specialists say secure them against any infection conceivable to limit possible ailment during the pandemic.
For those more than 12, get inoculated against COVID-19 and seasonal influenza, to downplay the two ailments.
“Kindly get immunized for this season’s virus and COVID-19 — please,” Michelson said. “It is significant for you, for the kids and for everybody.”
She added that children under a half year old can’t have influenza chances, so it’s significant that grown-ups and youngsters do as such to assist with keeping babies solid.
“So the more grown-ups who get immunized, the more uncertain it will be for weak infants under a half year to get seasonal influenza,” she said. “So another justification for why everybody ought to get inoculated is to assist with securing newborn children (under) a half year old.”
5.Influenza antibodies are especially significant this season to hold back from overpowering medical clinics.
In many pieces of the country, medical clinics are as of now overpowered with COVID-19 patients. The southernmost district in Illinois this week announced no accessible ICU beds due to flooding COVID-19 rates.
“We are hearing reports that individuals can’t get the consideration they need,” Michelson said. “Anything we can do to keep individuals out of the clinic will be useful. This is one more significant justification for individuals to get seasonal influenza antibody.”
6.Influenza immunization rates are by and large not excessively incredible.
Less than half of American grown-ups regularly have seasonal influenza chance every year, as per the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases. The philanthropic association dispatched a study last year, and tracked down that 59% of grown-ups surveyed wanted to get the flu antibody during the 2020-2021 influenza season, an increment from 52% the earlier year.
Of the people who were uncertain or not intending to get inoculated, 34% didn’t really accept that seasonal influenza antibody functioned admirably, 32% said they never got this season’s virus, 29% were worried about expected incidental effects and 22% said they were stressed over getting seasonal influenza from the vaccination — however that is unrealistic. Influenza shots are produced using either the inactivated infection or a solitary protein from the infection, and can’t cause sickness, as indicated by the CDC.
7.There’s been a focus on immunizations — and antibody reluctance — during the pandemic, yet specialists aren’t sure what this may mean for influenza shot take-up this season.
“I might dare to dream it will urge more individuals to get inoculated against flu,” Korpics said. “Flu, as COVID, is a preventable disease because of our capacity to inoculate. As a doctor, it is extraordinarily dismal to see patients who go to the clinic and pass on from flu or COVID, which might have been forestalled by the immunization.”
She noticed that even patients who get this season’s virus or COVID-19 after inoculation by and large have a substantially more gentle sickness are as yet shielded from hospitalization, extreme ailment and demise.
Michelson refered to an April study in the diary JMIR Public Health and Surveillance that found among an example of individuals in the United Kingdom that “Coronavirus has expanded acknowledgment of flu immunization in beforehand qualified however unvaccinated individuals and has propelled generous take-up in recently qualified individuals.”
However, she added the proviso that the United Kingdom has an alternate populace and culture than the United States, so it’s difficult to gauge the number of individuals will have influenza chance here this season.
“I truly think this is difficult to anticipate,” she said. “I trust that individuals will understand that COVID antibodies are in a real sense saving great many lives each day and that influenza immunizations can do likewise.”
8.While it’s difficult to tell seasonal influenza and COVID-19 separated, there are a few contrasts in manifestations.
Loss of taste or smell, for instance, is frequently connected with COVID-19 however far-fetched with seasonal influenza, wellbeing specialists say. Yet, body hurts, fevers, cerebral pains and exhaustion are manifestations of both infections. Wellbeing authorities prompt getting tried for COVID-19 at whatever point suggestive.

 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks ago
 Sports4 weeks ago
Sports4 weeks ago
 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks ago
 Business4 weeks ago
Business4 weeks ago
 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks ago
 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks ago
 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks ago
 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks ago