Science
SpaceX postpones Starlink launch as ocean outmatches drone ship as improves
Published
5 years agoon
By
Mark David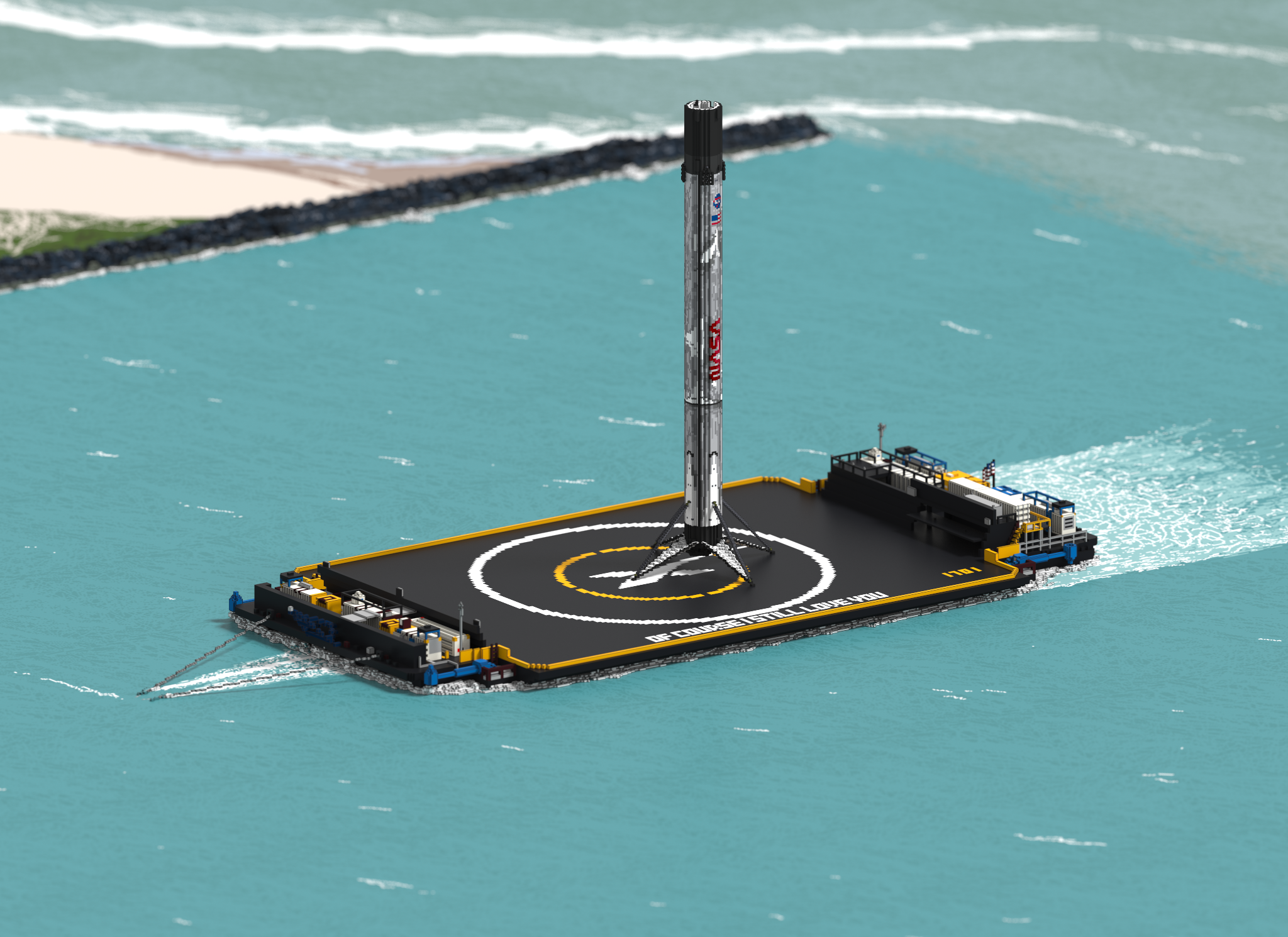
SpaceX’s thirteenth Starlink dispatch has been inconclusively postponed by “severe weather in the recovery area, later clarified by CEO Elon Musk as instance of the automaton transport losing its fight with the sea.
Initially booked to dispatch as ahead of schedule as September seventeenth, Starlink-12 – the twelfth Starlink v1.0 mission – was pushed to September eighteenth about an hour prior to takeoff. SpaceX didn’t offer an explanation at that point however is currently revealing that climate in the recuperation zone (Atlantic Ocean) was to be faulted for the 24-hour reuse and the inconclusive dispatch postpone that followed before long.
President Elon Musk went further, uncovering that the SpaceX drone transport relegated to Starlink-12 couldn’t hold its situation in solid Atlantic Ocean flows, constraining the organization to postpone the mission uncertainly. Until conditions improve in SpaceX’s automaton transport recuperation zone, the organization will probably be not able to dispatch Starlink missions. Musk, nonetheless, as of now has an answer as a primary concern.
In a similar tweet, Musk uncovered that SpaceX implies for its automaton transport “thrusters to be upgraded for future missions,” a clearly instinctive reaction to ramble ships being overwhelmed by sea flows. There’s one basic issue, however: drone transport Just Read The Instructions, a similar boat right now unfit to hold its situation in (as a matter of fact solid) sea flows, finished broad overhauls only a modest bunch of months back.
Preceding those redesigns, JRTI and OCISLY were adequately indistinguishable – both brandishing a couple of unassuming generators and four generally little station-keeping engines (splendid blue). After the greater part a time of work, drone transport JRTI came out the opposite end with significantly bigger azimuth engine units and in any event a few times the force yield. The space past automaton transport JRTI’s promoter arrival deck has been pretty much filled to the edge with new generators.
As it were, shy of some major auxiliary changes or a littler landing zone for Falcon promoters, it’s difficult to envision how SpaceX could generously overhaul Just Read The Instructions’ as of now redesigned generators and engines.
In drone transport JRTI’s safeguard, the Eastern seaboard is as yet feeling the leftovers of Hurricane Sally simultaneously as Hurricane Teddy is only a couple of days away. Just ~48 hours from now, Starlink-12’s Falcon 9 sponsor landing zone will be dependent upon 30-40 mph (50-70 km/h) winds and pinnacle wave statures of 15 feet (~4.5m) in the shadow of Teddy. The oceans in that district will probably stay unsound for promoter arrivals until September 24th or 25th at the soonest without significant changes in momentum estimates.
Ebb and flow atmosphere models don’t really foresee an expansion in the recurrence of Atlantic Ocean storms because of a worldwide temperature alteration, albeit warming will probably support the power of most typhoons to a significant degree. All things considered, it’s somewhat of a wash in the case of putting vigorously in emotional automaton transport execution overhauls would really be justified, despite all the trouble for Falcon sponsor recuperation, given that the hurricane season just endures a small amount of the year. In the event that SpaceX needs to reliably dispatch 50-100+ times each year out of Florida, it’s probable an easy decision.
Notwithstanding, if SpaceX seeks after overhauls a long ways past Just Read The Instructions’ present arrangement, it will be interesting to perceive what the organization’s two workhorse drone ships wind up resembling. On the off chance that current figures hold, Starlink-12 is probably not going to dispatch until late one week from now, a postpone that has pushed Starlink-13 (already NET late September) into October.
Mark David is a writer best known for his science fiction, but over the course of his life he published more than sixty books of fiction and non-fiction, including children's books, poetry, short stories, essays, and young-adult fiction. He publishes news on apstersmedia.com related to the science.

You may like
-


Elon Musk Unveils Grok-3: A Game-Changing AI Chatbot to Rival ChatGPT
-


SpaceX to Launch 21 Starlink Satellites from Florida on February 4
-


SpaceX will begin a busy year for moon missions this week with the launch of two private lunar landers
-


Elon Musk’s AI company raises $6 billion from AMD, Nvidia, BlackRock, and other investors
-


Crew Dragon Mission Delay Extends Astronauts’ Stay on ISS by a Month
-


Boeing Starliner crews will have an extended stay on the ISS due to SpaceX’s delay
Science
China’s Tianwen-2 Set for Launch to Asteroid and Comet
Published
3 months agoon
February 21, 2025
China has taken a major step forward in its deep-space exploration efforts as the Tianwen-2 spacecraft arrived at the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Sichuan province for final launch preparations. The China National Space Administration (CNSA) confirmed the development on February 20, 2025, signaling that the mission is on track for its scheduled launch in the first half of the year.
A Dual-Purpose Mission
The Tianwen-2 mission is a combined near-Earth asteroid sample return and comet rendezvous mission, marking another ambitious endeavor for China’s space program. The mission is set to launch aboard a Long March 3B rocket, with a tentative liftoff expected around May 2025.
The primary target of Tianwen-2 is the near-Earth asteroid Kamoʻoalewa (2016 HO3), a small celestial body with a diameter estimated between 40 to 100 meters. The asteroid is considered a quasi-satellite of Earth, meaning it follows a co-orbital path with our planet. Scientists believe Kamoʻoalewa might be a fragment of the Moon, ejected into space after an ancient impact event.
After collecting samples from Kamoʻoalewa, the main spacecraft will continue its journey to comet 311P/PANSTARRS, a celestial body that exhibits both asteroid-like and comet-like characteristics. By studying these two objects, scientists aim to gain valuable insights into the composition, evolution, and history of the solar system, including the distribution of water and organic molecules.
Launch Preparations Underway
CNSA stated that the launch site facilities are fully prepared, and pre-launch tests are proceeding as planned. Engineers and scientists are meticulously working to ensure the spacecraft is ready for its complex mission, which will involve multiple orbital maneuvers, sample collection, and deep-space travel over nearly a decade.
Sampling Kamoʻoalewa: Two Innovative Techniques
To collect material from Kamoʻoalewa, Tianwen-2 will employ two advanced sampling methods:
- Touch-and-Go (TAG) Method – This technique, used by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx and JAXA’s Hayabusa2 missions, involves briefly touching the asteroid’s surface to gather samples.
- Anchor-and-Attach System – This approach uses drills attached to the spacecraft’s landing legs, allowing for a more stable and secure extraction of subsurface material.
Early mission concepts, when Tianwen-2 was initially known as Zheng He, indicated that China aimed to collect between 200 and 1,000 grams of asteroid samples. These samples will help scientists analyze Kamoʻoalewa’s mineral composition, origin, and potential similarities with lunar material.
Challenges in Sample Return
Although China has successfully executed two lunar sample return missions—Chang’e-5 (2020) and Chang’e-6 (2024)—returning asteroid samples presents unique challenges. Unlike the Moon, Kamoʻoalewa has negligible gravity, requiring specialized landing and sampling techniques. Additionally, the reentry module carrying the samples will experience higher velocities, demanding advanced thermal protection and parachute deployment systems.
To address these challenges, the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) conducted high-altitude parachute tests in 2023, ensuring the safe return of asteroid samples to Earth around 2027.
Comet Rendezvous: Studying 311P/PANSTARRS
Returning samples from Kamoʻoalewa will not mark the end of Tianwen-2’s mission. The spacecraft will execute a gravitational slingshot maneuver around Earth, propelling it toward comet 311P/PANSTARRS in the main asteroid belt. The rendezvous is expected around 2034.
311P/PANSTARRS is considered a transitional object between asteroids and comets, making it an ideal candidate for studying the origins of cometary activity within the asteroid belt. Scientists hope to analyze its orbit, rotation, surface composition, volatile elements, and dust emissions, shedding light on the evolution of comets in the inner solar system.
Scientific Instruments on Board
The Tianwen-2 spacecraft is equipped with a suite of cutting-edge instruments to study its targets, including:
- Multispectral and infrared spectrometers – To analyze surface composition.
- High-resolution cameras – To map geological features in detail.
- Radar sounder – To probe subsurface structures.
- Magnetometer – To search for residual magnetic fields.
- Dust and gas analyzers – To examine cometary activity.
- Charged particle detectors – To study interactions with the solar wind (developed in collaboration with the Russian Academy of Sciences).
China’s Expanding Deep-Space Ambitions
Tianwen-2 follows the highly successful Tianwen-1 Mars mission, which saw China land the Zhurong rover on Mars in 2021. The Tianwen series is a key part of China’s growing presence in deep-space exploration:
- Tianwen-3 – A Mars sample return mission, scheduled for 2028–2030.
- Tianwen-4 – A Jupiter system exploration mission, launching around 2030, featuring a solar-powered orbiter for Callisto and a radioisotope-powered spacecraft for a Uranus flyby.
Chinese researchers have emphasized the importance of asteroid sample return missions, citing their potential for groundbreaking scientific discoveries and the development of new space technologies.
With Tianwen-2, China is taking a bold step into the future of deep-space exploration. By returning samples from an asteroid and studying a comet, the mission will provide crucial insights into the origins of the solar system and planetary evolution. As launch preparations continue, the world eagerly anticipates another milestone in China’s space program.
Science
SpaceX to Launch 21 Starlink Satellites from Florida on February 4
Published
4 months agoon
February 3, 2025
SpaceX plans to launch another batch of Starlink satellites into orbit from Florida’s Space Coast on February 4, 2025. The mission will deploy 21 Starlink satellites, including 13 equipped with direct-to-cell communications capabilities, marking another major step in SpaceX’s ambitious plan to provide global high-speed internet coverage.
The Falcon 9 rocket flight from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station is scheduled to take place during a roughly three-hour launch window that opens at 3:37 a.m. (0837 GMT). SpaceX will livestream the event on its X account (formerly Twitter), with coverage beginning about five minutes before liftoff.
The mission will use the experienced Falcon 9 first-stage rocket, which will be making its 21st launch and landing. According to SpaceX, this rocket has already flown on 20 missions, 16 of which were dedicated Starlink launches. If all goes as planned, the rocket will return to Earth about eight minutes after liftoff, landing on the unmanned “Just Read the Instructions” craft in the Atlantic Ocean.
The Falcon 9 upper stage will continue its journey to deploy 21 Starlink satellites into low Earth orbit (LEO) about 65 minutes after liftoff. This will be SpaceX’s 15th Falcon 9 mission in 2025, with nine flights dedicated to expanding the Starlink constellation.
Direct-to-cell capabilities
A notable feature of this mission is the inclusion of 13 Starlink satellites with direct-to-cell capability. These advanced satellites are designed to enable seamless connectivity for standard mobile phones, eliminating the need for specialized hardware. This technology has the potential to revolutionize communications in remote and underserved areas, providing reliable internet and cellular services directly to users’ devices.
The growing Starlink constellation
SpaceX is rapidly expanding its Starlink network, which is already the largest satellite constellation ever assembled. In 2024 alone, the company launched more than 130 Falcon 9 missions, about two-thirds of which were dedicated to Starlink deployments. According to astrophysicist and satellite tracker Jonathan McDowell, SpaceX currently operates nearly 7,000 Starlink satellites in LEO.
The Starlink network aims to provide high-speed, low-latency internet access to users around the world, especially in regions lacking traditional infrastructure. With this latest launch, SpaceX is expanding the network’s capacity and coverage, bringing its dream of global connectivity closer to reality.
Recyclability and sustainability
The Falcon 9 rocket’s first-stage booster exemplifies SpaceX’s commitment to reusability, a key factor in reducing the cost of spaceflight. By successfully landing and reusing the rocket, SpaceX has revolutionized the aerospace industry and set a new standard for sustainable space operations.
However, the rapid expansion of the Starlink constellation has raised concerns among astronomers and environmentalists. The growing number of satellites in LEO has created problems such as light pollution, which can interfere with astronomical observations, and space debris, which poses a threat to other spacecraft. SpaceX is actively working to mitigate these issues by implementing measures such as blacking out satellite surfaces and responsibly deorbiting inactive satellites.
The February 4 launch is part of SpaceX’s broader strategy to achieve global internet coverage and support its growing customer base. With the addition of direct-to-cell-connect satellites, the company is poised to offer even more versatile and simple connectivity solutions.
As SpaceX pushes the boundaries of space technology, the world will be watching to see how the Starlink network evolves and addresses the challenges associated with large-scale satellite constellations. For now, the focus is on the upcoming launch, which will mark another milestone in SpaceX’s journey to connect the world.
Science
Scientists Trap Molecules for Quantum Tasks, Paving the Way for Ultra-Fast Tech Advancements
Published
4 months agoon
January 22, 2025
In a groundbreaking milestone for quantum computing, researchers from Harvard University have successfully trapped molecules to perform quantum operations. This achievement marks a pivotal advancement in the field, potentially revolutionizing technology and enabling ultra-fast computations in medicine, science, and finance.
Molecules as Qubits: A New Frontier
Traditionally, quantum computing has focused on using smaller, less complex particles like ions and atoms as qubits—the fundamental units of quantum information. Molecules, despite their potential, were long considered unsuitable due to their intricate and delicate structures, which made them challenging to manipulate reliably.
However, the latest findings, published in the journal Nature, change this narrative. By utilizing ultra-cold polar molecules as qubits, the researchers have opened up new possibilities for performing quantum tasks with unprecedented precision.
A 20-Year Journey to Success
“This is a breakthrough we’ve been working toward for two decades,” said Kang-Kuen Ni, Theodore William Richards Professor of Chemistry and Physics at Harvard and senior co-author of the study.
Quantum computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations exponentially faster than classical computers. It has the potential to solve problems that were once deemed unsolvable.
“Our work represents the last critical piece needed to construct a molecular quantum computer,” added co-author and postdoctoral fellow Annie Park, highlighting the significance of this achievement.
How Molecular Quantum Gates Work
Quantum gates, the building blocks of quantum operations, manipulate qubits by taking advantage of quantum phenomena like superposition and entanglement. Unlike classical logic gates that process binary bits (0s and 1s), quantum gates can process multiple states simultaneously, exponentially increasing computational power.
In this experiment, the researchers used the ISWAP gate, a crucial component that swaps the states of two qubits while applying a phase shift. This process is essential for creating entangled states—a cornerstone of quantum computing that allows qubits to remain correlated regardless of distance.
Overcoming Long-Standing Challenges
Earlier attempts to use molecules for quantum computing faced significant challenges. Molecules were often unstable, moving unpredictably and disrupting the coherence required for precise operations.
The Harvard team overcame these obstacles by trapping molecules in ultra-cold environments. By drastically reducing molecular motion, they achieved greater control over quantum states, paving the way for reliable quantum operations.
The breakthrough was a collaborative effort between Harvard researchers and physicists from the University of Colorado’s Center for Theory of Quantum Matter. The team meticulously measured two-qubit Bell states and minimized errors caused by residual motion, laying the groundwork for even more accurate future experiments.
Transforming the Quantum Landscape
“There’s immense potential in leveraging molecular platforms for quantum computing,” Ni noted. The team’s success is expected to inspire further innovations and ideas for utilizing the unique properties of molecules in quantum systems.
This advancement could significantly alter the quantum computing landscape, bringing researchers closer to developing a molecular quantum computer. Such a system would harness the unique capabilities of molecules, opening doors to unprecedented computational possibilities.
The Road Ahead
The implications of this achievement extend far beyond academia. By unlocking the potential of molecules as qubits, the researchers have taken a vital step toward creating powerful quantum computers capable of transforming industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to financial modeling.
As researchers continue to refine this technology, the dream of a molecular quantum computer—one that capitalizes on the complexities of molecular structures—moves closer to reality. This breakthrough represents not just a leap forward for quantum computing but a glimpse into the future of technology itself.